INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer disease is a progressive Neurodegenerative disorders which affects memory and cognitive functions by gradually destroying the brain cells. AD does not cause death directly, but significantly it increases the risk of complications that may eventually lead to death.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) AD was classified as the seventh leading cause of death in the United States in 2022, while COVID-19 ranked fourth. (1) There is no cure for AD at this time, but various treatments are there to reduce and control some of its symptoms.
In terms of anatomical pathology AD is defined by two key points:
1. Senile plaques which are extracellular deposits of Beta amyloid protein.
2. Neurofibrillary tangles made up of phosphorylated tau proteins that are present in neurons. (2)
Majority of the cases of AD are commonly seen in people of age 65 or older and the chances of developing the disease rises with increase in age.
STAGES OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE:
STAGE 1: The early symptomatic phase, which lasts for several year.
STAGE 2: The middle stage includes forgetting personal care and family names.
STAGE 3: The late stage is characterized by difficulty walking, lack of awareness of place and time, etc.
SYMPTOMS
- Memory loss that affects daily activities and tasks.
- Difficulty in recognizing familiar faces or places.
- Disorientation to time and place is common
- Trouble in planning or solving problems.
- Difficulty in completing familiar tasks.
- Impaired judgement.
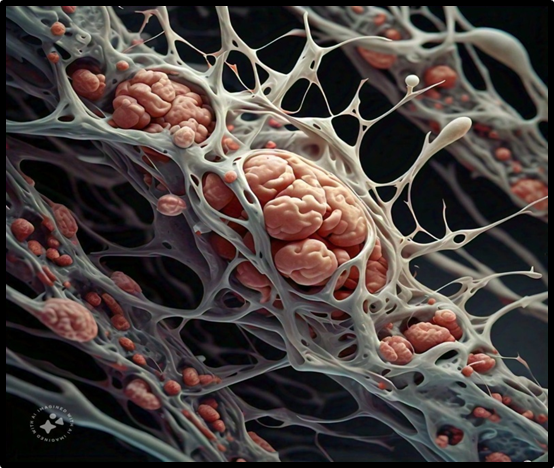
Fig. Accumulation of Beta Amyloid in Brain Neurons.
RISK FACTORS OF AD
- GENETIC INHERITANCE
- AGEING
- EXPOSURE TO ALUMINIUM
- TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
- VASCULAR DISEASE
- MUTATION IN AMYLOID PRECURSOR PROTEIN
DIAGNOSIS
Nowadays, biofluid markers such as (amyloid beta, phosphorylated tau protein, neurofilament tangles (NFT) and amyloid precursor protein (App)) are performed in the brain to diagnose AD.
Various others tests are performed to diagnose AD like:
- CSF Test: This test is recommended to measure the levels of amyloid and tau proteins in fluid.
- Blood sampling.
- MRI and PET SCAN: MRI is done to generate the detailed image of brain.
- CT SCAN
TREATMENT
Due to the complicated nature of AD there is no specific treatment and the available drugs are designed to manage the symptoms and slow the progression of disease
- FDA approved medications to manage symptoms:
- Brexpiprazole: Molecular formula: C25H27N3O2S
- Donepezil: Molecular formula: C24H29NO3
- Galantamine: Molecular formula: C17H21NO3
- Memantine: Molecular formula:C12H21N
- Rivastigmine: Molecular formula:C14H22N2O2

REFERENCE
1. Ahmad FB, Cisewski JA, Xu J, Anderson RN. Provisional Mortality Data – United States, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 May 05;72(18):488-492. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
2. Shinohara M, Sato N, Shimamura M, Kurinami H, Hamasaki T, Chatterjee A, et al. Possible modification of Alzheimer’s disease by statins in midlife: interactions with genetic and non-genetic risk factors. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:71.Article PubMed PubMed